Biodiversity holds the web of life together like rivets in an airplane wing. Just as each missing rivet ups the chance for trouble, so does every species lost from an ecosystem. People everywhere rely on nature’s offerings: clean water, crop pollination, food resources.
Yet these systems falter if biodiversity weans under human pressure like Kenya’s Lake Turkana where wildlife abounds but faces threats from over fishing and climate shifts leading to dwindling fish stocks and compromised support for local communities.

What is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity, in its essence, refers to the wide mix of plants, animals and microorganisms that exist. Each species has a role in an ecosystem; together they maintain life’s balance. Richness varies from dense rain forests to stark deserts but is essential everywhere for healthy habitats.
It allows systems to work better against shocks or stressors like disease outbreaks or climate shifts. Biodiversity also means genetic variety within each species which helps them adapt over time. Through thickets of greenery and microscopic worlds unseen by us thrive countless relationships each vital as threads holding the web we live on intact a cornerstone ensuring our world flourishes.
Read Also : Importance of forest
Importance of Biodiversity?
Biodiversity’s role in our world is crucial. Species coexist, forming ecosystems that uphold life’s balance. Our very existence hinges on nature for necessities: food, homes, pure water and medicine sources.
Ecosystems lend vital services like pollination and climate control that we depend upon heavily every day without even realizing it often times. Yet human actions threaten this natural mosaic activities strain ecosystem integrity critically. Reports highlight a steep wildlife decline; since the 1970s species numbers plummeted by an average of 68%.
Alarmingly, extinction looms over a million plant and animal kinds globally. Still hope endures with concerted global conservation drives showing promise a testament to humanity’s potential for nurturing biodiversity back from the brink.
Variety of Life Forms and Essential Ecosystem Services
Life brims with variety, from tiny bugs to big animals. Each being fits into a web that keeps our world running. Plants give us food and air while bees keep them growing by moving pollen around.
Wetlands clean water as it flows toward the sea; forests take in bad air, giving back good for you and me. These services are vital; they support life’s show. Without this complex balance, much would go wrong below.
All beings play parts even ones we don’t see keeping soils rich and oceans lively can be key. In sum: diversity fosters health across land, sky, and wave a treasure house of life we must learn to save.
Read Also: Importance of nature
Genetic Diversity Significance and Natural Resource Wealth
Genetic diversity within species is nature’s safety net. It allows for resilience in changing conditions, much like a varied investment portfolio cushions against market volatility. The Irish potato famine showed the perils of relying on one crop type; when blight struck, there was no fallback, leading to widespread hunger and displacement.
In fish conservation too, diverse genes mean health for aquatic populations across years. Some thrive while others lag but overall survival isn’t threatened – this is the ‘portfolio effect’. Salmon in southeast Alaska exemplify how different spawning times nature’s bet-hedging strategy ensure species steadiness even as climates shift unexpectedly.
Conserving genetic variety thus becomes crucial in our unstable world where adaptability equates to continued existence.
Resistance to Environmental Changes
Biodiversity loss can hit ecosystems hard, much like global warming or pollution. Researchers from top institutions warn that with fewer plant species, our natural world faces big risks. When we lose 1 to 20 percent of plant types, the impact seems small.
But as losses grow to 21-40 percent and beyond up to half of all species the harm is just as bad as other environmental threats humanity has created: think ozone holes or acid rain on forests. Scientists once thought biodiversity’s decline was a minor issue but now place it high among factors changing our planet for good; they advise taking this into serious account when tackling environmental policies. The future health of ecosystems and by extension ours may depend on how well we preserve the variety within nature’s green fabric.
Species Interdependence Balance
Species interdependence refers to the critical balance where each life form relies on others for survival. In a balanced ecosystem, different species provide services crucial for mutual existence. Take earthworms they enhance soil fertility, which in turn supports plant growth and maintains healthy habitats.
Diverse genes within species bolster their populations against extinction while fostering robust ecosystems capable of recovering from disasters like deforestation or drought. Conservation strategies highlight this key relationship by promoting sustainable practices that respect our biological diversity. Destroying natural variety not only impacts individual organisms but also undermines ecological functions necessary for all life forms, including humans.
Therefore, maintaining biodiversity is essential for sustaining nature’s delicate equilibrium and ensuring long-term viability of environments worldwide.
Health Benefits from Biodiversity
Biodiversity brings vast health benefits. It fuels ecosystem services crucial for clean water, food, and fuel all vital to our well-being. With species loss, these services falter; this can hit human health hard.
Diminished biodiversity also threatens the discovery of medical advances since many treatments stem from nature’s genetic storehouse. Diverse diets rich in different plants and animals bolster nutrition and overall health levels; a drop in variety could mean less micronutrient intake. Furthermore, traditional medicines relied on by over half the globe’s people often come from wild flora that needs preserving as part of our natural wealth.
Plainly put: Protecting diverse life forms is essential for sustaining not just the planet’s health but ours too.
Cultural and Aesthetic Value
Biodiversity’s cultural value links to our shared heritage, beliefs, and practices. It shapes identities through traditional knowledge passed down for ages. Many cultures draw inspiration from nature for art, music, and literature; it gives us joy in beauty beyond function or food.
Its aesthetic worth is seen in the diverse landscapes we cherish vast forests like the Amazon brimming with life forms. This natural tapestry enriches our experience of a world steeped in color and variety that many seek out as essential soul nourishment. A robust ecosystem also safeguards treasured habitats against disasters while maintaining climate balance making biodiversity critical not just ecologically but culturally too.
Economic Growth Support
Biodiversity backs economic vigor. Firms use nature’s goods; we rely on these assets for growth, even survival. Data from World Bank and partners like Malaysia’s central bank show stark ties between finance and ecosystems over half of loans back businesses needing intact habitats to thrive.
Yet, our actions harm this wealth source depleting it risks futures. Natural capital accounting reveals such impacts by valuing resources properly in national accounts. By grasping how land, waterways impact economies through systematic measurement, decision-makers can steer investments towards sustainable practices that bolster both economy and environment.
In low-income nations especially, natural riches form a huge wealth portion vital for their prosperity leap forward.
Climate Stability Agents
Climate stability agents are natural systems that keep our world’s weather in check. Forests, oceans, and wetlands act much like sponges or shields. They soak up carbon from the air; this helps slow warming trends.
These areas cool local climates too trees give shade and water bodies bring down heat. Experts note how vital these ecosystems are for life on Earth. Loss of such places spells trouble: more floods, droughts, storms hit us hard when nature’s balance tips.
Protecting these agents is a must do task to ensure we have stable seasons and healthy environments moving ahead.
Scientific Research Opportunities
For science, vast opportunities abound for those eager to explore biodiversity’s secrets. Researchers look deep into ecosystems, tracking how species adapt and survive. They study genes, seeing how life’s code varies from place to place.
Teams map out habitats, noting which are most at risk and need protection fast. We can better understand nature’s web by learning about life in forests and oceans. This web is a complex, fragile tapestry that we must handle with care to preserve its essence.
Diverse ecosystems provide food, clean water, and air. They guard against extreme weather and support human health.
Every species plays a part in this balance; their loss can lead to unforeseen consequences affecting us all. Protecting varied life forms ensures nature’s resilience vital for future generations’ survival.
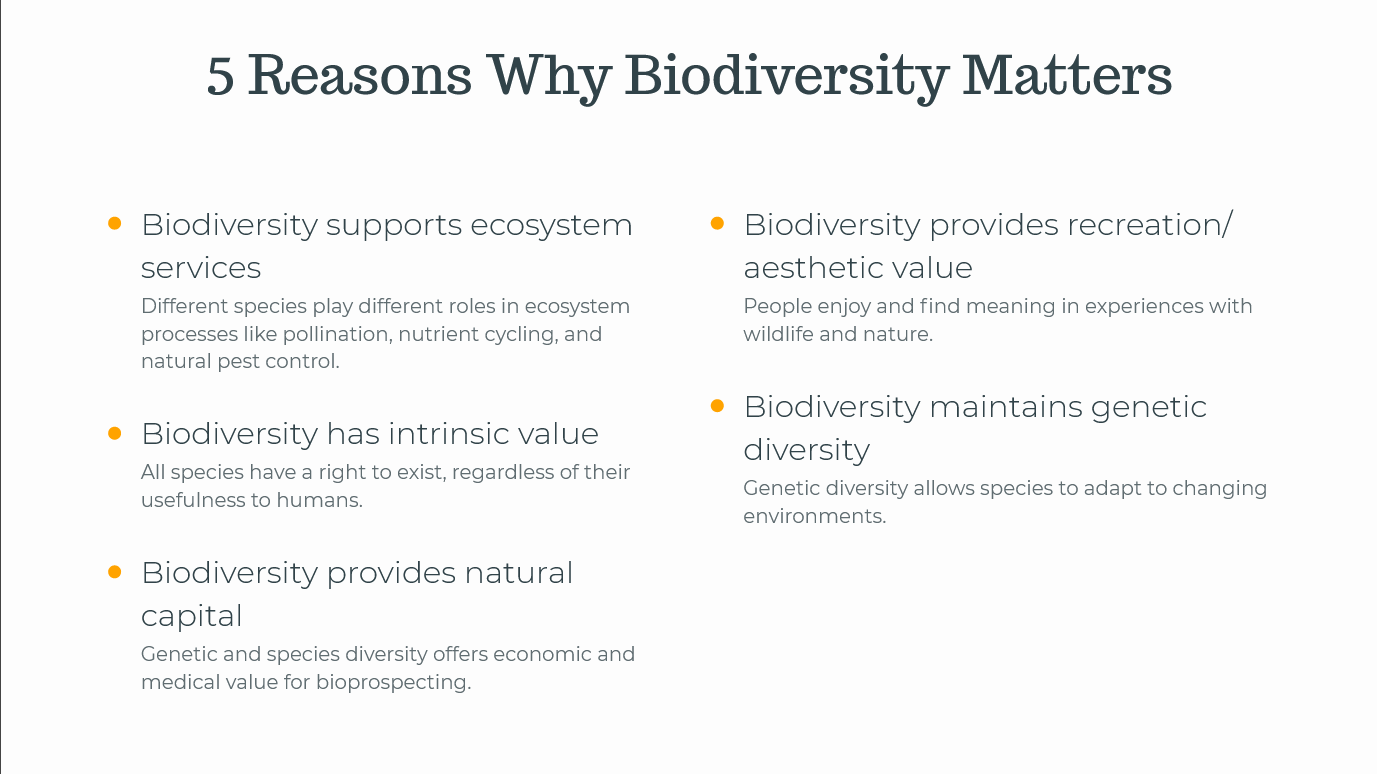
Importance of Biodiversity Slides



References:
https://www.conservation.org/blog/why-is-biodiversity-important
https://www.amnh.org/research/center-for-biodiversity-conservation/what-is-biodiversity
https://www.reelpaper.com/blogs/reel-talk/why-is-biodiversity-important-to-ecosystems
https://www.usgs.gov/news/why-genetic-diversity-important
https://www.nsf.gov/news/news_summ.jsp?cntn_id=124016
https://www.globalissues.org/article/170/why-is-biodiversity-important-who-cares
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/biodiversity-and-health
https://sdwatch.eu/2020/12/the-value-of-biodiversity/
https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/immersive-story/2022/12/07/securing-our-future-through-biodiversity
https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rstb.2019.0104
https://royalsociety.org/news-resources/projects/biodiversity/why-is-biodiversity-important/